Jump to heading Module 7–01 Rectangular Coordinate System
Jump to heading 1.Coordinate Relationships Between Two Points
- Points on the coordinate axis don't belong to any quadrant.
- Points on x-axis
. - Points on y-axis
.
- Points on x-axis
Jump to heading 2.Coordinates of the Midpoint Between Two Points
- The coordinates of the midpoint between two points
and are . - Special case: The midpoint between point
and the origin is . - Formula derivations
- Special case: The midpoint between point
Jump to heading 3.Distance Formula Between Two Points
- The distance between two points
and is . - Special case: The distance between point
and the origin is . - Formula derivations
Jump to heading 4.Focus 1
Midpoint formula
- Analyze using the midpoint formula
.
Jump to heading
Jump to heading Solution
Jump to heading Conclusion
- Derived Solution
According to the Solution, get, so choose . - Formula used
Jump to heading 5.Focus 2
Distance formula
- Analyze using the distance formula
.
Jump to heading
Jump to heading Solution
Jump to heading Conclusion
- Derived Solution
According to the Solution, get, so choose . - Formula used
Jump to heading
Jump to heading Solution
Jump to heading Conclusion
- Derived Solution
According to the Solution, get, so choose . - Formula used
- Additionally, if the problem is an isosceles right triangle
Jump to heading Module 7–02 Straight Line
Jump to heading 1.Angle of Inclination
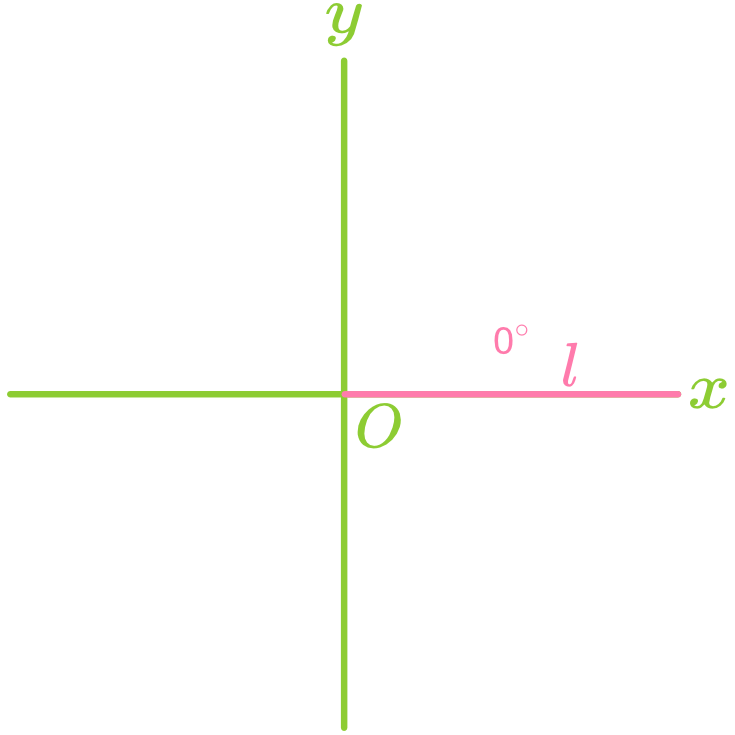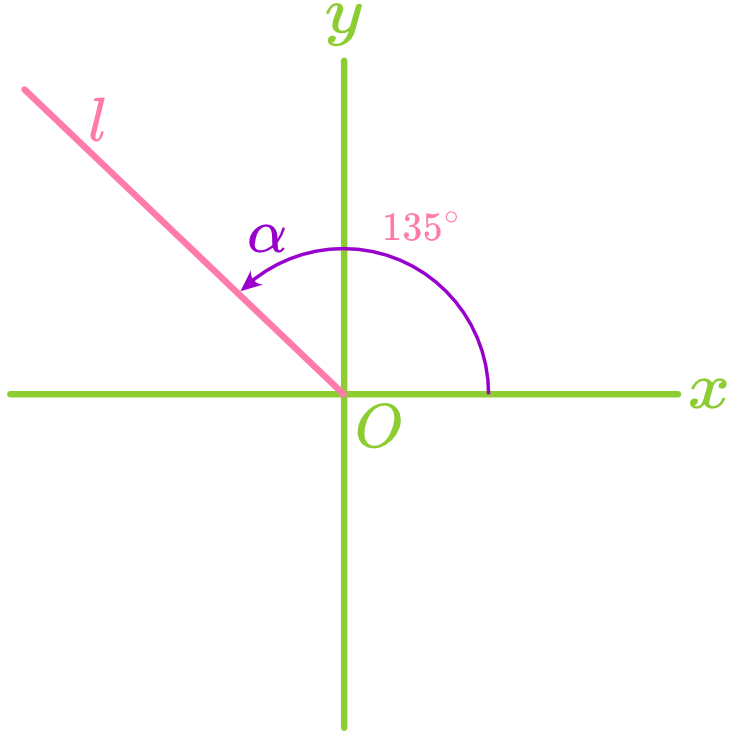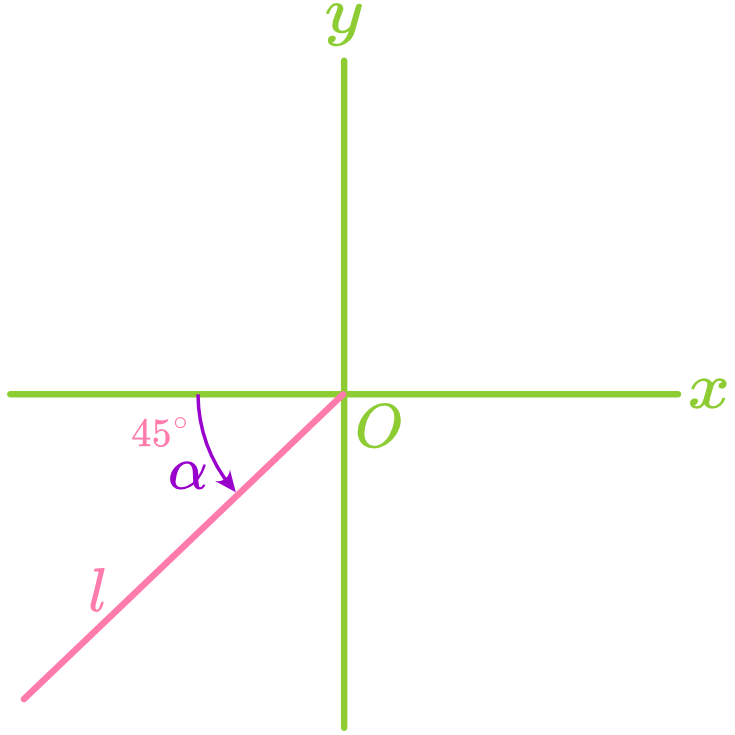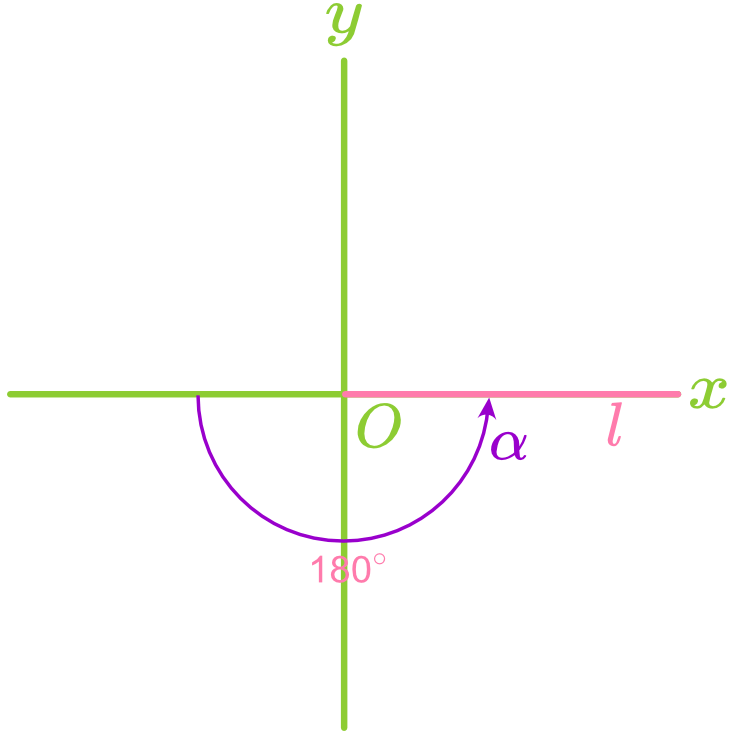
The angle formed between a straight line and the positive direction of the x-axis is called the angle of inclination, denoted as
, where . Note: When a line is horizontal, its angle of inclination is
. When a line is vertical, its angle of inclination is . - Counterclockwise rotation increases
. - Clockwise rotation decreases
.
- Counterclockwise rotation increases
Jump to heading 2.Definition of Slope
The tangent of the inclination angle is the slope, denoted as
. Remarks:
- When
; Zero numerator - When
; - When
, is undefined; Zero denominator - When
;
- When
Jump to heading 3.Common Inclination Angles and Slope
- Supplementary angles: their tangents are opposite numbers.
.
| Inclination Angle | Slope |
|---|---|
Jump to heading 4.Two-Point Slope Formula
Let there be two points
and in a straight line , then . Special cases:
- If
, the line is horizontal, and . - If
, the line is vertical, and undefined. Jump to heading The slope between
and is .
- If
Jump to heading 5.Focus 1
Inclination angle and slope
- Pay attention to special inclination angels, such as
, and observe the sign and magnitude changes of the slope.
Jump to heading
Jump to heading Solution
Jump to heading Conclusion
- Derived Solution
According to the Solution, get, so choose . - Formula used
Counterclockwise rotation:
.
Clockwise rotation:. - The size of
indicates the steepness of the line. - The larger
is, the steeper the line becomes. - The smaller
is, the flatter the line becomes.
- The larger
- The size of
Jump to heading
Jump to heading Solution
Show known conditions
Jump to heading Conclusion
- Derived Solution
According to the Solution, get, so choose . - Formula used
Jump to heading 6. Equation of a Line
Jump to heading
- If the slope
and the are known, the equation of the line can be expressed as . - Special cases:
Jump to heading
(Passing through the origin) (Horizontal line)
Jump to heading
- If the slope
and a point are known, the equation of the line can be expressed as or . - Special case:
The point-slope form becomes the slope-intercept form. - Equation derivations
Jump to heading
If the x-axis and y-axis intercepts are known to be
Jump to heading
If the coordinates of two points
- Special case:
- The intercept form is a special case of the two-point form.
- The two-point form can be changed into the point-slope form.
- Equation derivations
Jump to heading
The above equations can all be transformed into a linear function
, which is called the general form of the equation of a line. Jump to heading Remark: The general form is very important, as it allows you to quickly calculate the slope
. derivations
Jump to heading Quickly calculate the Intercept form
Special case:
Jump to heading
(Horizontal line) (Vertical line) (Line passing through the origin)
Jump to heading 7.Focus 2
Equation of a line
- Master the various forms of the equation of a line and their applicable situations, and understand the differences between the different forms of the equation.
Jump to heading
Jump to heading Solution
Jump to heading Conclusion
- Derived Solution
According to the Solution, get, so choose . - Formula used
- Line representation of the equation of a straight line
Equations Horizontal Line Vertical Line Line Passing Through the Origin Other Lines Slope-intercept form ✅ ❌ ✅ ✅ Point-slope form ✅ ❌ ✅ ✅ Intercept form ❌ ❌ ❌ ✅ Two-point form ❌ ❌ ✅ ✅ General form ✅ ✅ ✅ ✅
Jump to heading
Jump to heading Solution
Collinearity of three points
Any two points have the same slope They Can't form
Jump to heading Conclusion
- Derived Solution
According to the Solution, get, so choose . - Formula used
Jump to heading
Jump to heading Solution
Jump to heading Conclusion
- Derived Solution
According to the Solution, get, so choose . - Formula used
- Opposite intercepts and equal Intercepts
- The intercepts are opposites.
①.
② Passes through the origin. - The intercepts are equal.
①.
② Passes through the origin.
- The intercepts are opposites.
Jump to heading
Jump to heading Solution
Solve using the point-slope form
Solve using the three-point collinearity method
Jump to heading Conclusion
- Derived Solution
According to the Solution, get, so choose . - Formula used
Jump to heading
Jump to heading Solution
Show known conditions
Jump to heading Conclusion
- Derived Solution
According to the Solution, get, so choose . - Formula used
- Additionally, If the problem is to calculate the area of the triangle formed by the intercept form
Jump to heading 8.Focus 3
The line passes through quadrants
- Analyze the graph based on the slope and intercepts of the line.
- Remember the conclusion: When
, the line must pass through the first and third quadrants; when , the line must pass through the second and fourth quadrants.
Jump to heading
Jump to heading Solution
Jump to heading Conclusion
- Derived Solution
According to the Solution, get, so choose . - Formula used
| Platforms | Courses | Coursewares |
|---|---|---|
| YouTube | Watch | Courseware |
| Dailymotion | Watch | |
| Rumble | Watch |